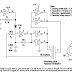
VGA to TV Converter Circuit
This converter circuit basically takes VGA signals and converts it to RGB + composite sync signal which can be fed to TV via SCART connector. VGA card picture components RED, GREEN and BLUE are already at the correct voltage level (0.7Vpp) and has correct impedance (75 ohm) for direct connection to correspondign inputs in the TV.
VGA to TV Converter Ciruit
VGA to TV Converter Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
For combining separate horizonal and vertical sync signal from VGA card to one composite sync signal needs a sync signal conversion which is feed to TV video in pin in SCART connector. The tv converter circuit has also sends correct level signal to the TV RGB input enabling control pin in the SCART connector (pin 16).
The circuit is simply based on one TTL chip with four XOR ports, two resistors and two capacitors. TTL chip was logical choise because VGA sync signals are TTL level signals.
The sync signal combiner has a system to adjust to different sync polarities so that it always makes correct composite sync signals. VGA card uses different sync signal polarities to tell the monitor which resolution is used. This circuit adjusts to sync signal polarity changes in less than 200 milliseconds, which is faster than setting time of a normal VGA monitor in the display mode change. The tv converter circuit needs well regulates +5V (+/-5%) power supply and takes about 120 mA current.
VGA to TV converter parts list are as follow:
Main circuit
U1 74LS86 (74HC86 or 74HCT86 can also be used)
C1 22 microfarads 16V electrolytic capacitor
C2 use 47 uF 16V electrolytic for more reliable operation (22 uF listed schematic can cause problems in some cases)
R1,R2 2.2 kohm, 1/4 W
R3,R4,R5 2.2 kohm, 1/4 W
R6,R7,R9 47 ohm, 1/2 W
R8 120 ohm, 1/2 W
T1,T2 BC547B (2N2222 should also work but note the different pinout)
P1 15 pin SUB-D connector (DE-15)
Output connector
21 pin EURO/SCART connector
Wiring:
Red, Green, Blue and Composite Sync lines should be wired using 75 ohm coaxial cable for best picture quality, but can be replaced with normal shielded wire.
Power supply components
7805 regulator chip
100 uF electrolytic 25V
10 uF electrolytic 16V
100 nF polyester or ceramic condensator
Wall adapter which outputs 8-18V DC and 150 mA or more current
Connector for connecting wall adaptor to circuit
Source: http://www.tkk.fi/Misc/Electronics/circuits/vga2tv/circuit.html